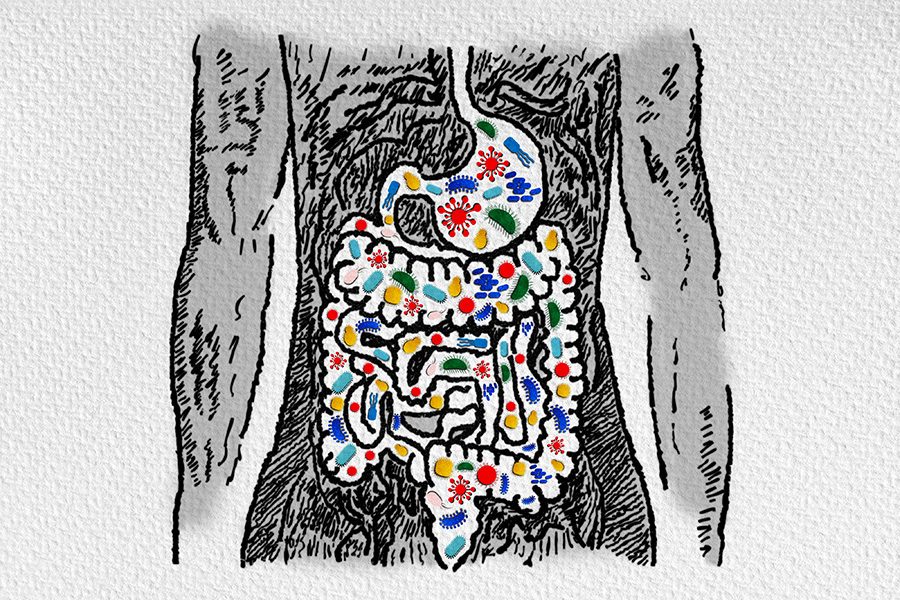
The gut microbiome refers to the community of microorganisms that live in the human digestive tract. These microorganisms include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes. The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in human health, influencing everything from digestion to immunity to mental health. In this blog, we will explore the importance of the gut microbiome and how it affects our overall health and the growing evidence that suggest that the gut microbiome may play a role in spinal cord injury wellness and possible recovery.
Studies have shown that following SCI, there are significant changes in the gut microbiome, including alterations in the composition and diversity of the microbial community. Additionally, animal studies have suggested that manipulating the gut microbiome can affect SCI outcomes, such as inflammation and motor function recovery.
One potential mechanism for this correlation is the gut-brain axis, which is a bidirectional communication system between the central nervous system and the gastrointestinal tract. Through this pathway, the gut microbiome can influence the immune system, neural function, and inflammation, which are all important factors in SCI recovery.
While more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between the gut microbiome and SCI recovery, the existing evidence suggests that targeting the gut microbiome could be a promising therapeutic strategy for improving outcomes following SCI.
What Does the Gut Microbiome Do?
The gut microbiome is incredibly diverse, with trillions of microorganisms living in the digestive tract. The majority of these microorganisms are bacteria, and they play a vital role in breaking down food and producing essential nutrients. When we eat, the bacteria in our gut break down the food and produce short-chain fatty acids, which provide energy to the cells lining the gut. These fatty acids also help to maintain a healthy gut lining and prevent inflammation.
In addition to digestion, the gut microbiome also plays a crucial role in the immune system. The microorganisms in the gut help to regulate the immune response and prevent harmful bacteria from taking over. They also produce antimicrobial peptides that help to kill harmful bacteria and viruses.
Furthermore, recent research has shown that the gut microbiome can affect our mental health. The microorganisms in the gut produce neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, which are important for regulating mood and behavior. Studies have found that people with depression and anxiety have different gut microbiomes than those without these conditions. This suggests that the gut microbiome may play a role in mental health disorders.
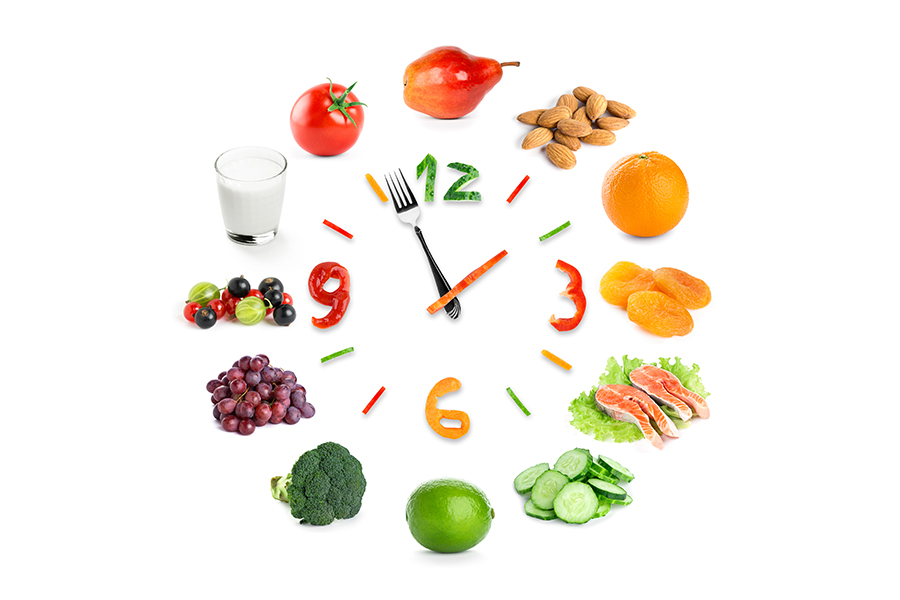
So, how can we maintain a healthy gut microbiome? One of the most important things we can do is eat a healthy diet. A diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables can help to promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. On the other hand, a diet high in processed foods and sugar can lead to an overgrowth of harmful bacteria.
Another way to support a healthy gut microbiome is through probiotics and prebiotics. Probiotics are live bacteria that can be found in fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut. Prebiotics, on the other hand, are a type of fiber that feeds the beneficial bacteria in the gut. Prebiotics can be found in foods such as garlic, onions, and bananas.
In conclusion, the gut microbiome is a complex and essential part of human health. It influences everything from digestion to immunity to mental health. By eating a healthy diet and incorporating probiotics and prebiotics into our daily routine, we can support a healthy gut microbiome and improve our overall health and wellbeing.
In Gut Health,
Aaron